The term neurotransmitter refers to the molecules that are used by the body’s nervous system to send messages between its neurons.
Your nervous system is a vast network of nerves that can send and receive signals from different cells in your body. These are responsible for controlling various functions, such as your mind and muscles. Your body’s nervous system also receives and uses information from other organs and sources, and this constant feedback is vital to its function.
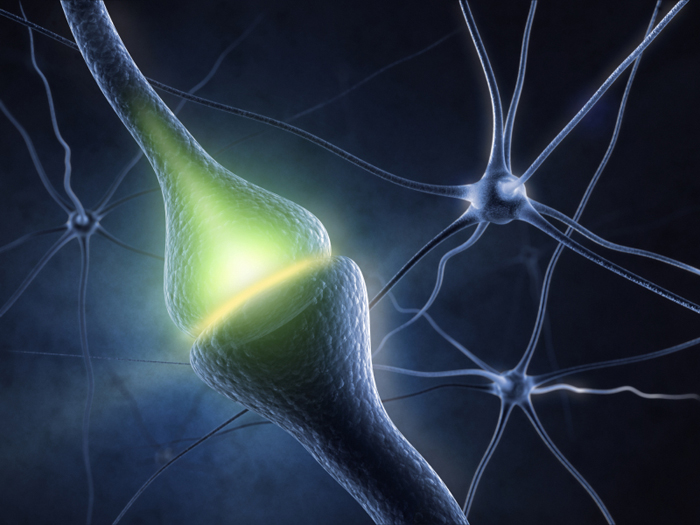
When two neurons communicate, they do so through the synaptic cleft, which is a small gap between the two synapses of each neuron. Through the release of certain chemicals, the signals are converted into chemical ones, which then trigger a specific response in one of the receiving neurons. The three different ways that a neurotransmitter affects a neuron are: excitatory (for excitatory signals), inhibitory (for inhibitory signals), and modulatory.
An excitatory transmitter causes an electrical signal to be generated in the receiving neuron, whereas an inhibitory one stops it. The receptor that a neurotransmitter binds to determines whether it is an inhibitory or excitatory substance.
Unlike the other types of neurotransmitters, neuromodulators are not limited to the synaptic cleft and can affect a large number of neurons at once. They regulate the populations of neurons by operating at a slower rate.
Most neurotransmitters are composed of amino acids, neuropeptides, or small amine molecules. Scientists are still trying to understand the interactions between these chemical messengers and their various functions in the nervous system.
What are the 7 main neurotransmitters?
The main neurotransmitters that are responsible for the majority of work in the nervous system are the seven small molecule ones. These include dopamine, acetylcholine, glutamate, serotonin, norepinephrine, gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), and histamine.
Key neurotransmitters
The first known neurotransmitter was identified by scientists as a small molecule known as Acetylcholine. It plays a vital role in the regulation of various functions in the peripheral and central nervous systems. In addition, it can maintain cognitive function.
In the central nervous system, glutamate is regarded as the primary excitatory neurotransmitter. On the other hand, major inhibitory neurotransmitters include the derivative of amino acid GABA, which is found in the spinal cord, and glycine.
Dopamine is a monoamine. This neurotransmitter is known to have numerous pathways in the brain, and it plays a variety of functions, such as motivation and motor control.
Another type of monoamine is known as norepinephrine. It is regarded as the main neurotransmitter that plays a role in the sympathetic nerve system, where it helps control the actions of various organs within the body.
Serotonin is another neurotransmitter that can be found in the brain and plays a variety of functions. Some of these include memory, appetite, and sleep.
Histamine is the last major monoamine. It plays a variety of roles in the body, such as regulating temperature and metabolism.
What are the 3 functions of a neurotransmitter?
The chemical messengers known as neurotransmitters are responsible for carrying messages between different parts of the body.
Why is neurotransmitter important?
The molecules known as neurotransmitters, which are the chemical messengers of the body, are the ones responsible for sending messages between two or more neurons.
What are the most important neurotransmitters?
The major neurotransmitters that are commonly associated with various disorders such as schizophrenia and Alzheimer’s disease are dopamine, serotonin, and glutamate.

Recent Comments