Benzoic acid is a phencyclic amine substance and the active ingredient in Benzo Fury. Benzoic acid, an organic amine substance that has stimulant, depressant, and analgesic properties. It can be found in a wide range of foods including wine, mushrooms, beef, chicken, milk, cheese, spinach, ginger, turmeric, and ginger. 6-APB can also be derived from the labelling agents used to label foods containing benzoic acid. Benzoic acid can also be administered orally as a treatment for a range of diseases and ailments including depression, dementia, chronic pain, herpes, nausea, Parkinson’s disease, urinary tract disorders, and ringing in the ears (1).
Benzoic Acid and its Originality
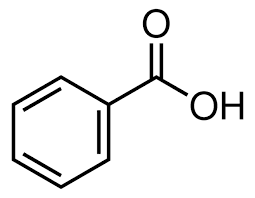
Benzoic acid was originally developed as a pharmaceutical preparation and was given the trade name “benzoic”. It was first used to treat serious burns and injuries that resulted in discoloration of the skin. Later medical workers started to use it for nerve and brain damage due to toxic chemicals such as ammonia, chlorine, and mercaptans produced during combustion. In the 1800s, it was discovered that benzoic acid reduced symptoms of nerve damage in animals, and it was used to treat nerve injuries suffered by soldiers in the Civil War (2).
The compound has several chemical structures, including a cysteine base, a bromine base, and three amino acids, as well as several aromatic compounds which contribute to its psychostimulant properties. It has a C-9 glycosyl base which produces energy when converted to ammonia, and a urine amino acid which produces a calming effect when metabolized into dopamine. It also contains a residue which produces an inactive form of the substance (3).
Test With Animals
Benzoic acid was first subjected to animal testing in which it was found to have positive effects on locomotion, memory, and behavior, as well as increasing the reaction time of several animals. More studies were conducted and the substance was then decided to be approved by the US Food and Drug Administration. In 1998, it was finally approved as a prescription drug for ADHD and sedative uses. Subsequently, many other disorders were found to have similar chemical properties. It is now being investigated for its potential psychological effects in a range of other diseases and conditions.
ADHD and sedative APB drugs are generally used for minor dental and gum problems or to alleviate anxiety and restlessness in patients undergoing neuroleptic therapy. Some patients also experience symptoms of depression. These drugs work by reducing hyperactivity and improving focus, although they do not cure the condition. Some of the symptoms of ADHD include lack of concentration, hyperactivity, distractibility, impulsivity, and forgetfulness. They are usually prescribed by pediatricians to treat the emotional and physical symptoms of ADHD.
A call for future research
Although their use is widely accepted, it is not entirely clear how benzoic acid works on the brain. The drug may stimulate the production of neurotransmitters, particularly dopamine and norepinephrine. They increase the levels of these neurotransmitters in the brain. It is believed that the drug improves the functioning of several areas related to attention and impulse control. They are also used off-label to treat depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, and chronic pain. It is not clear how these effects are manifested in patients.
Like all medicines, there are some possible side effects of taking this compound. Some of these side effects are dizziness, headache, insomnia, hallucinations, fast heart rate, and nausea. There is also a possibility that these could be reduced if the dosage is reduced.
Because they can be highly addictive, it is very important that you follow the recommended dosing schedule to avoid physical dependence. You should also avoid driving or operating machinery while taking the medication. If you must drive while under the influence of APB, you should do so cautiously and only after the doctor’s advice. The above-mentioned symptoms can also appear in people with a history of depression and other mental disorders.


Recent Comments